VSAT is short for very small aperture terminal, an earthbound station used in satellite communications of data, voice and video signals, excluding broadcast television. A VSAT consists of two parts, a transceiver that is placed outdoors in direct line of sight to the satellite and a device that is placed indoors to interface the transceiver with the end user’s communications device, such as a PC. The transceiver receives or sends a signal to a satellite transponder in the sky. The satellite sends and receives signals from a ground station computer that acts as a hub for the system. Each end user is interconnected with the hub station via the satellite, forming a star topology. The hub controls the entire operation of the network. For one end user to communicate with another, each transmission has to first go to the hub station that then retransmits it via the satellite to the other end user’s VSAT. VSAT can handle up to 56 Kbps.
VSAT applications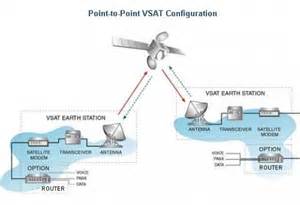
Possible VSAT applications include: point of sale, Internet access, file distribution, database access, environmental monitoring, police, customs and excise offices. Capacity is not a problem with both very small to very large networks all viable. Growth is possible in small steps thus keeping costs related to actual use. VSAT systems provide a both data and, if required, voice services. Voice or data services with the possibility of communication between all sites (i.e. in mesh mode connection) requires slightly larger antennas and/or transmitter power amplifiers. Mesh networks may be attractive for telephony applications such as remote industry, hotel chains, bases, exploration, disaster, emergency relief etc.
VSAT systems are attractive where the coverage area is large, where quick installation is required and where terrestrial alternatives are difficult to organise.
ionospheric Faraday rotation occurs, which causes severe interference in linear polarised systems. Typical C band dish sizes are 1.8m, 2.4m, 3.8m. Doubling the dish area halves the power you need from the satellite and should achieve big cost savings on your monthly charges. If you are a town ISP it is generally better to spend more on the dish and save on the monthly charges.
Smaller Ku band spot beam are provided by many satellite and enable smaller dishes to be used by customers.
Satellite internet terminals
General purpose VSAT terminals are now becoming common. These essentially provide broadband internet access and allow web browsing and emails. Costs can be quite low if your burst speed bit rate capacity is shared with many other terminals using the same satellite capacity. For example 30 VSATs may all share the same 512k down / 64k up capacity. This works fine for internet browsing but is unsuited to Voice calls or video streaming which would cause congestion. If VoIP is required then higher monthly cost dedicated continuous information rate (CIR) service is preferred.